This post is also available in:
 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
The adoption of blockchain technology – decentralized ledgers, smart contracts – is gaining traction across many different sectors. It is inevitable that military organizations across the globe will want to ensure they stay ahead of the curve.
Blockchain already has various military applications, as suggested by coincentral.com:
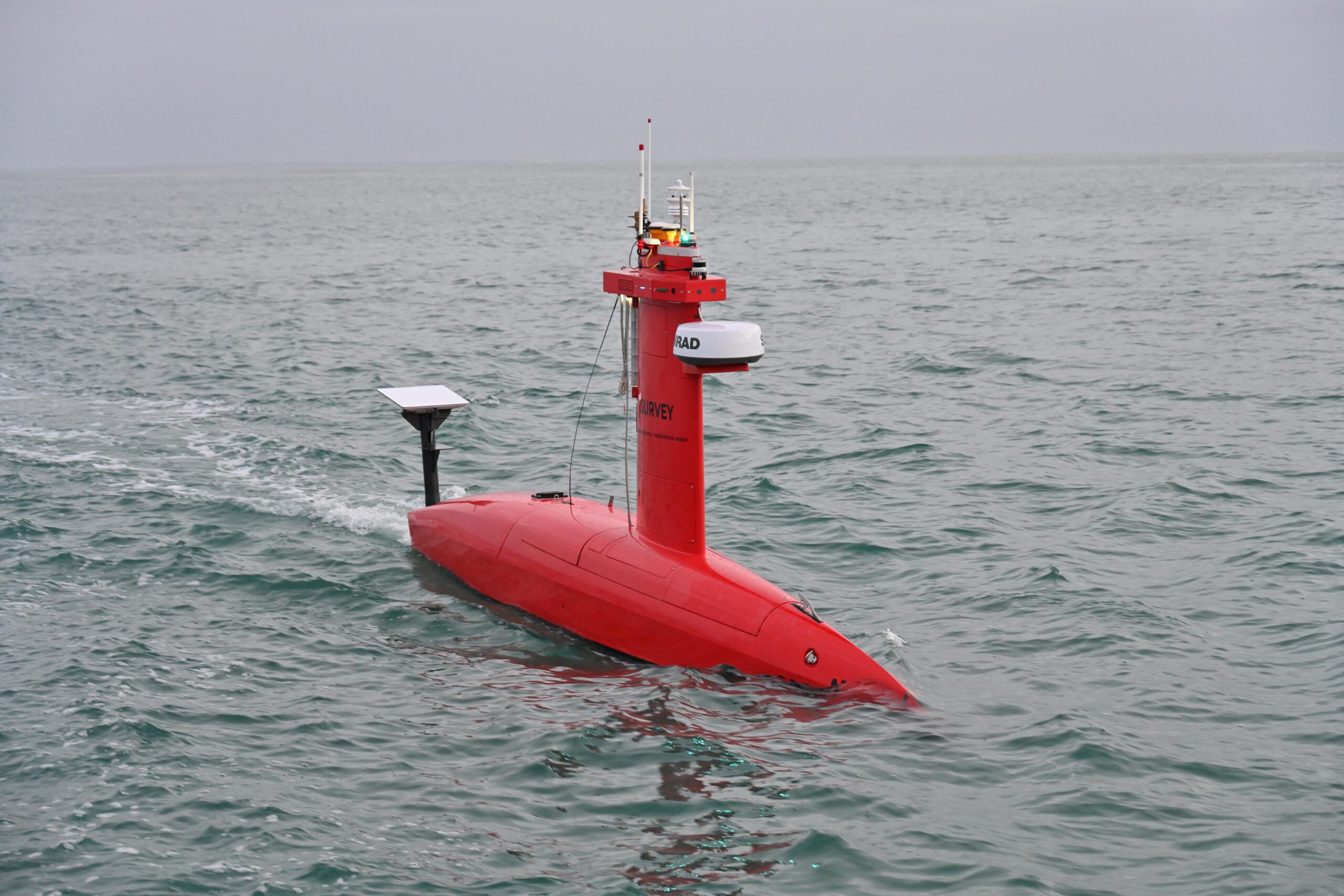
- Drones – The convergence of AI and blockchain with drone technology creates formidable possibilities in blockchain military applications. In addition to analyzing and reporting on footage in real time, AI can power autonomous drones. These can fly entirely independently, without any intervention or control needed from a human. Blockchain can record the data collected by AI-powered drones immutably and in real time. It can also record the flight decisions and actions taken by the drone. With each drone operating as part of a decentralized network, then if it is later destroyed, whatever it has collected or performed would still be recorded on the blockchain.
- Battleship control system – Battleships are equipped with a vast array of different armaments, that must work together seamlessly. This relies on sensory technology integrated with the weapons control systems. The naval ships of many countries, including the US, Japan, and Spain rely on one system to do this – the Aegis Combat System, which have been powering naval battleships for the last five decades. It uses a complex system of radars and powerful computers to make split-second decisions. However, it has a crucial weakness – it is a centralized system, a single point of failure. Take down the Aegis, and you can take down the ship. Blockchain allows decentralization of computing power across multiple nodes, offering clear advantages for powering a system such as Aegis. Lockheed Martin, the manufactures the Aegis Combat System, recently partnered with Guardtime Federal to incorporate blockchain into Lockheed’s supply chain risk management, software development, and systems engineering processes. The company is the first US defense contractor to implement distributed ledger technology.
- Additive manufacturing (AM) is the military term for 3D printing. The US military builds prototypes and parts for weapons and vehicles using AM methods. Since 2017, the US Navy has committed to integrating blockchain within each step of an AM operation. Using a decentralized network in this way meets the requirements of the digital thread, i.e. it provides a secure, theoretically unlimited data store. It also allows the sharing of data across the entire AM process using the nodes in the network.