This post is also available in:
 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
In aviation maintenance, the direct cost of human-error is estimated at 10% of the total maintenance cost. For an airline operating a fleet of more than 1000 airplanes, this can add up to $500M annually, and more.
This problem goes beyond the servicing industry and includes industrial operation of complex equipment, decision-making in complex human-machine missions in defense, defensive cybersecurity in enterprises, and many more.
The root cause can often be attributed to the inability of humans to consistently identify, perform, and evaluate the outcomes of tasks correctly, even in simple task environments.
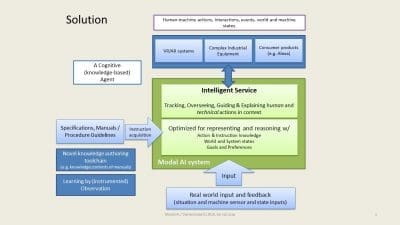
A cognitive agent for human-machine interaction
Modal AI, an Israeli startup participating at the iHLS Security Accelerator’s sixth cycle, develops a novel core AI technology for building cognitive agents, that supplies systems with action-oriented “mental” models, to help them become (self) aware of their own actions and action outcomes, as well as those of others – humans or machines.
Like humans, a cognitive agent is endowed with agency, an ability to reflect over, guide, oversee and cause actions to occur, as well as to critically evaluate achieved results, and perform remedial actions, as needed.
Having a cognitive agent to support work tasks is like having a knowledgeable colleague looking over one’s shoulders, and helps ensure correct task outcomes.
The advantages of a cognitive agent are many. For example:
Compliance: a cognitive agent can test for expected inputs and outputs and thereby assure that every performed human and machine activity step, whether it was completed correctly.
Guidance and Explanation: a cognitive agent can explain outcomes of actions. For example, why a repair task was evaluated as not correctly completed; or why an industrial process or equipment operation did not start, for example, due to failed preconditions. The agent can (then) also provide pro-active guidance on how to accomplish the task correctly, and what to do next.
Teachability and reduced development cost: Models can be created through instrumented observations. For example, instead of writing instructions for repairing an engine part, a virtual reality simulation can be used to demonstrate and label step by step instructions and outcomes. These can directly be inputted into cognitive agent.
The light weight symbolic inference algorithm further enables the agent to run low powered and cost edge device; and a unique “connecting the dots” capability can also be provided that hypothesizes about the intent of observed human actions and outcomes.
Application Areas and Use Cases
The company currently looks at a number of domains with the objective to identify collaboration with a strategic partner in creating a Minimal Viable Product (MVP) solution of value to them. Domains currently explored include:
⦁ industrial installation and maintenance, including in aerospace
⦁ operation of complex capital equipment
⦁ customer training and simulation in the use of complex capital equipment
⦁ defensive cyber security in enterprise systems
⦁ integrated citizenship services
A good technology fit is when world and machine state feedback, such as through log files, IoT-bases sensing or through other means, can readily be obtained. It’s there where this AI technology can shine and provide the most significant added value to task and business outcomes.
The company is currently looking for other use cases of value.


























