This post is also available in:
 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
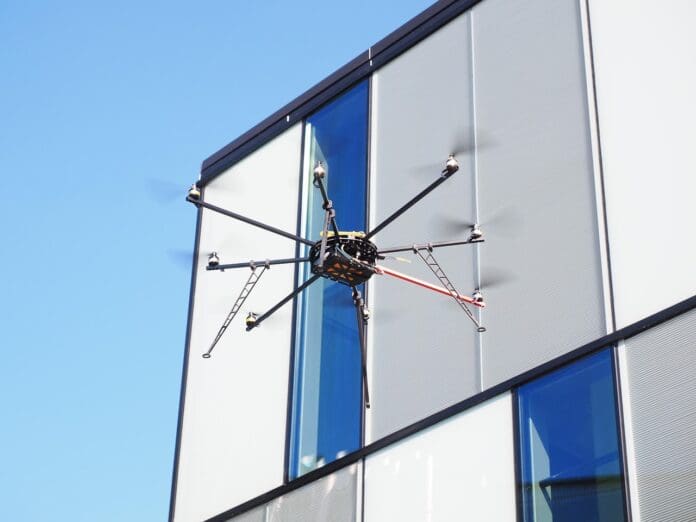
Researchers from the UK have proposed a groundbreaking idea where flying robots could be used to construct skyscrapers. This concept is built on an emerging technology known as Aerial Additive Manufacturing (Aerial AM), which allows drones to autonomously deposit materials in mid-air.
The study, a collaboration between Imperial College London and the University of Bristol, highlights how drones equipped with advanced manipulators could overcome the limitations of traditional construction methods. Aerial AM technology could allow construction to reach new heights, both literally and figuratively, by enabling the building of structures in areas that were once inaccessible, such as mountaintops or rooftops.
One of the primary advantages of using flying robots in construction is their ability to work in unrestricted spaces. Unlike ground-based systems, drones do not need fixed construction sites and can be deployed in swarms, providing flexibility and scalability in the building process. This could also reduce material consumption, lower transport distances, and significantly improve the safety of construction sites.
However, the technology is still in its early stages. According to the press release, the main challenges include ensuring material durability and achieving smooth coordination among multiple drones working together. While technologies such as robotic arms and 3D printing gantries are already in use on construction sites, they are typically large, immobile, and unsuitable for the environments in which drones have an advantage.
Currently being tested at DroneHub in Switzerland, part of the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology (EMPA), the technology shows promise for disaster relief efforts. Aerial robots could provide rapid response capabilities in disaster zones, delivering materials and constructing emergency shelters where traditional vehicles cannot reach.
With further development, these drones could become an essential tool for large-scale construction projects, offering a safer, more efficient way to build in challenging environments. The research team envisions a future where these flying robots autonomously optimize construction processes, making complex building projects faster and more cost-effective.