This post is also available in:
 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)
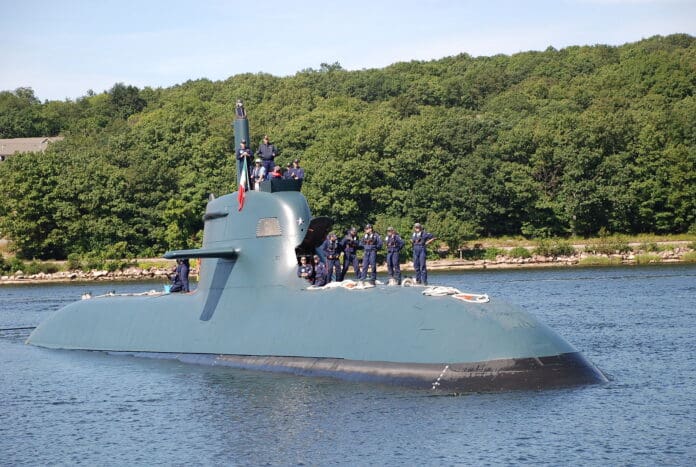
German shipbuilder thyssenkrupp Marine Systems (tkMS) is set to enhance the capabilities of the German Navy’s Type 212A submarines by integrating a lithium-ion battery system. This innovative battery technology, which has been in development since 2015 and underwent testing in 2019, marks a significant leap forward in submarine technology.
The integration of lithium-ion batteries promises numerous benefits. According to tkMS, these batteries will improve overall performance, offering enhanced battery capacity and increased operational range at improved speeds. Additionally, the lithium-ion technology is expected to provide a longer service life, addressing some of the limitations associated with traditional lead-acid batteries. These older battery systems, widely used since World War II, suffer from poor energy storage and delayed charging, which can hinder naval operations.
The HDW Class 212A submarine measures approximately 58 meters in length, displacing around 1,500 tons. It features six weapon tubes and can accommodate a crew of 28. This diesel-electric attack submarine is compact yet packed with advanced sensors, communication equipment, and weapon control systems. Its current design includes an HDW fuel cell system linked to a PERMASYN motor, which allows for extended submerged operations with minimal noise.
With the integration scheduled to begin in 2028, tkMS is working toward achieving ‘Parent Navy Approval’ for this technology. This approval will pave the way for incorporating lithium-ion systems into other existing and future submarine projects.
Other nations are also moving toward lithium technology in their naval fleets, according to Interesting Engineering. The Chinese PLA Navy has been testing lithium-ion batteries in its conventional submarines since 2022, seeking to replace aging lead-acid systems. Similarly, Japan has enhanced its battery safety by adding manganese to lithium designs, while South Korea launched its first lithium-powered submarine in 2021, employing nickel and cobalt-based batteries with additional safety measures.
As tkMS continues its advancements, the integration of lithium-ion batteries could redefine the operational capabilities of submarines, paving the way for more efficient and effective underwater missions.